Describe a Nonspecific Immune Defense Used by the Body
Nonspecific Resistance Innate Immunity The second line of defense is nonspecific resistancethat destroys invaders in a generalized way without targeting specific individuals. Others eg fever inflammation and interferon are produced by the host in response to infection.
Innate or nonspecific immunity is the defense system with which you were born.
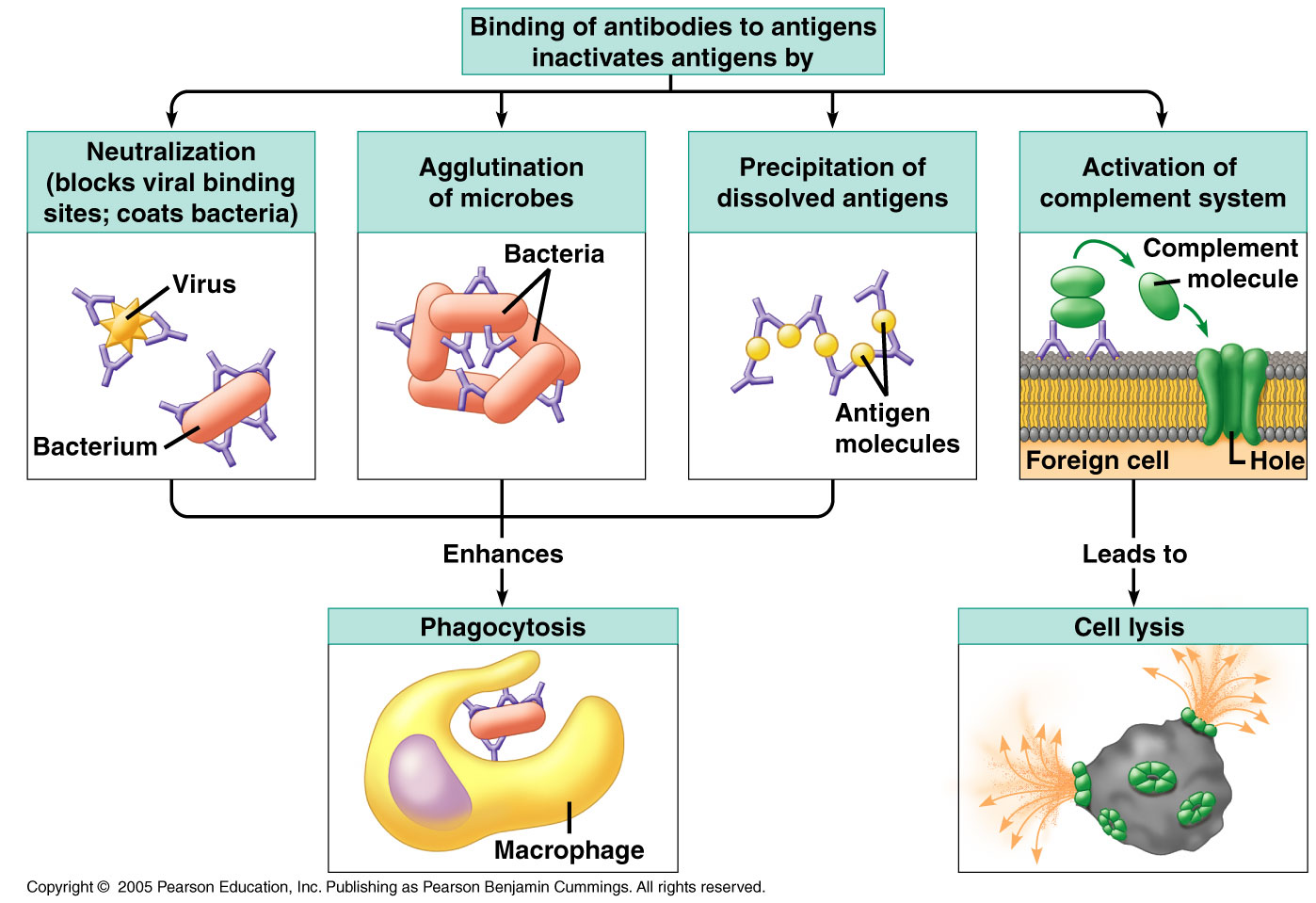
. The details of how these mechanisms operate to protect. All nonspecific defenses begin to act before the specific defense responses develop and can potentiate some of the. It protects you against all antigens.
Antimicrobial proteins phagocytes and other cells inhibit spread of invaders. For example macrophagesare cells derived from monocytesa type of white blood cell. Skin and Mucous membranes antimicrobial chemicals natural killer cells phagocytosis inflammation and fever.
These barriers form the first line of defense in the immune response. Nonspecific defenses include physical and chemical barriers the inflammatory response and interferons. Physical and chemical barriers prevent infection.
Innate nonspecific defense system. Physical barriers include the intact skin and mucous membranes. External body membranes skin and mucosae Second line of defense.
I Surface Membrane Barriers- skin and mucous membrane A. Acid Mantle pH 3-5 B. Nonspecific immunity and possible ways Innate immunity Physical Means These are as follows.
The innate immune system is the dominant system of host defense in most organisms and the only one in plants. Phagocytic cellsingest and destroy all microbes that pass into body tissues. Constitutes firstand second lines of defense.
Keratin resists physical stress resistant to weak acids and base 2. Non-specific human defence systems against disease The body is constantly defending itself against attacks from pathogens. Examples of innate immunity include.
This system does not confer long-lasting immunity against a pathogen. Intact skin is a barrier and prevents the entry of microorganisms while ulcerated skin is more prone to develop an infection. Immune system provides resistance to disease Made up of two intrinsic systems.
Enzymes in tears and skin oils. Intact mucous membranes are also a barrier to the entry of microorganisms. Membranes secrete protective chemicals 1.
An example of such a substance is lysozyme an enzyme present in tears that destroys the cell. The innate immune system is the bodys first line of defense against germs entering the body. Innate immunity involves barriers that keep harmful materials from entering your body.
Internal Defenses Second Line of Defense The body uses nonspecific cellular and chemical devices to protect itself 1. Non-specific immune cells function in the first line of defense against infection or injury. These barriers are aided by various antimicrobial chemicals in tissue and fluids.
The innate immune system provides this kind of nonspecific protection through a number of defense mechanisms which include physical barriers such as the skin chemical barriers such as antimicrobial proteins that harm or destroy invaders and cells that attack foreign cells and body cells harbouring infectious agents. Antimicrobial proteins in blood and tissue fluid. Innate immune defenses are non-specific meaning these systems respond to pathogens in a generic way.
The first line of defence. The phagocytes are the bodys fast acting first line of immunological defense against organisms that have breached barrier defenses and have entered the vulnerable tissues of the body. First line of defense.
A non-specific immune cell is an immune cell such as a macrophage neutrophil or dendritic cell that responds to many antigens not just one antigen. It responds in the same way to all germs and foreign substances which is why it is sometimes referred to as the nonspecific immune system. Some nonspecific defenses exist independently of infection eg genetic factors anatomic barriers nonspecific inhibitors in body fluids and phagocytosis.
Non-specific body defences The immune system defends humans from pathogens. Inflammatory response enlists macrophages mast cells WBCs and chemicals 4. The phagocytes of the immune system engulf other particles or cells either to clean an area of debris old cells or to kill pathogenic organisms such as bacteria.
Natural killer NK cells 3.
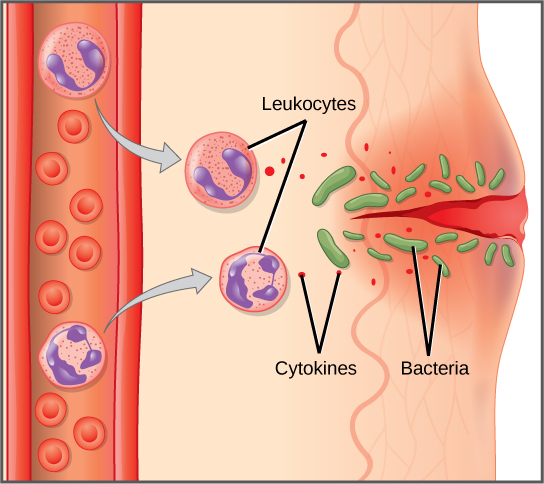
The Immune System Review Article Khan Academy
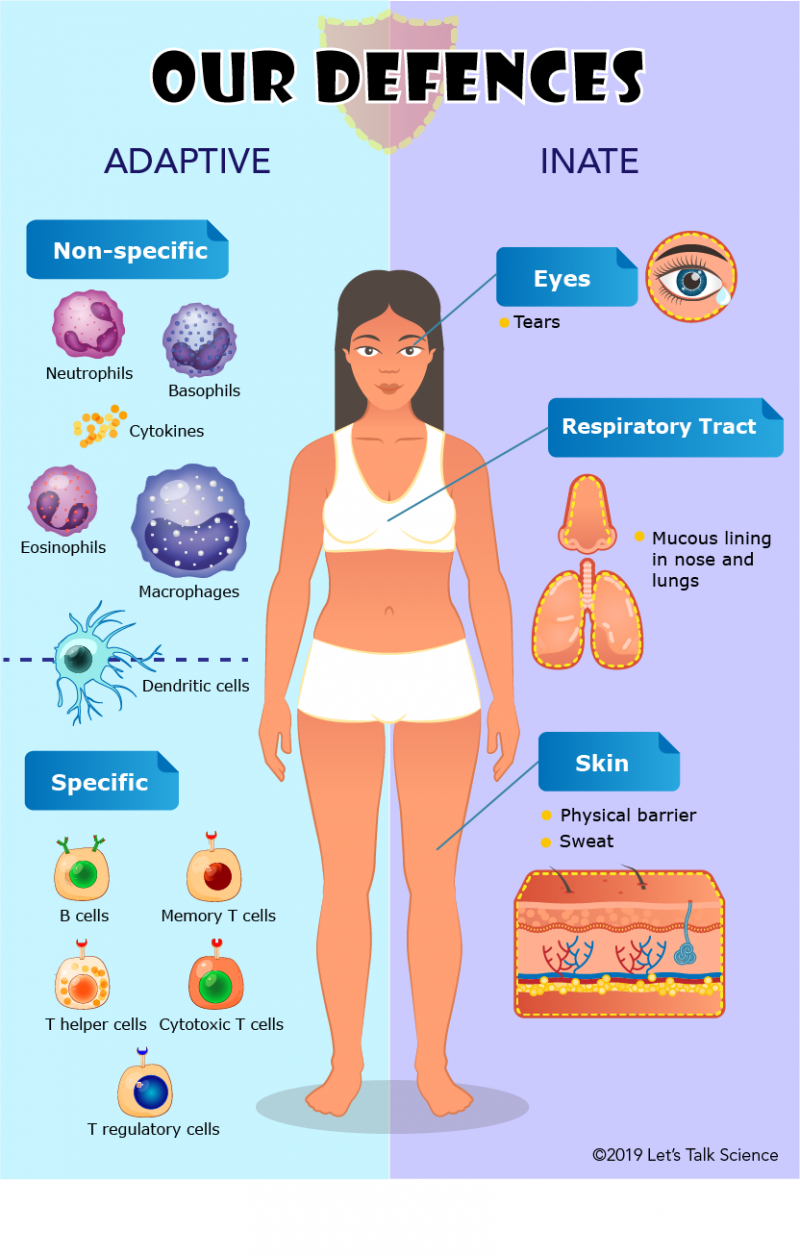
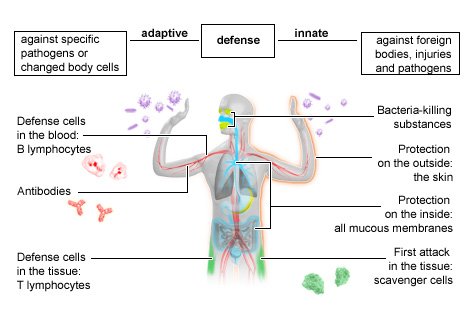
No comments for "Describe a Nonspecific Immune Defense Used by the Body"
Post a Comment